According to a 2017 Harvard Business Review article, researchers have found that the often-cited “80:20 principle” applies to workplace productivity. This principle simply means that the top 20% of employees contribute about 80% of the output in the typical workplace.

Shortly after the article was published, researchers with the OrgDev Institute conducted a meta-analysis to evaluate the 80:20 principle among organizations leveraging the REACH Ecosystem. The analysis included thousands of employees from a variety of industries including healthcare, retail, hospitality, mining, industrial, government, not-for-profit, professional services and more.
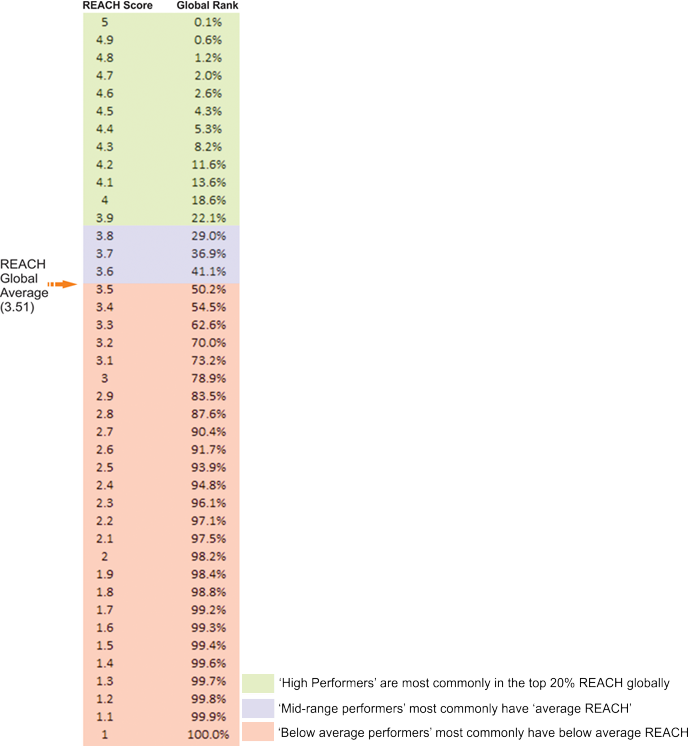
This meta-analysis reveals that REACH Quotient scores correlate with performance and reinforce the famed 80:20 principle.
Organisations that participated in each of the studies provided performance ratings for their employees (who had completed the REACH Profile). These ratings were categorized based on relative performance: below average performers, mid-range performers and top performers. The table overlays these performance categories with the distribution of average REACH Quotient scores.
While it is possible to be a top performer and not have a correspondingly high REACH Quotient score, the higher a person’s REACH Quotient score is, the more likely they are to be recognised as a top performer based on this global benchmark. The bottom line: people in the top 20% of REACH Quotient scores are more likely to be the top performers in their respective workplaces.

The good news is that REACH can be grown and that the development roadmap and resources needed to grow REACH are included in the REACH Ecosystem.
REACH Ecosystem capability and culture platform provides the tools to measure, then develop awareness, train, coach and reinforce learning to grow REACH of your people.